BCOM, BBA, CPA AND ACCA Students And Any Other Accounting Practitioners.
Understanding Intangible Assets – IAS 38 issued in march 2004
Intangible Assets

The objective of IAS 38 is to specify the accounting treatment for intangible assets not covered by another standard.
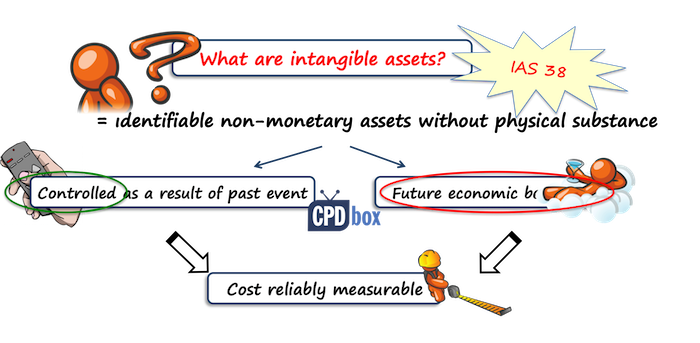
Intangible assets are assets without physical substance. Examples could be brand names, Licenses, patents, research and development expenditure etc.
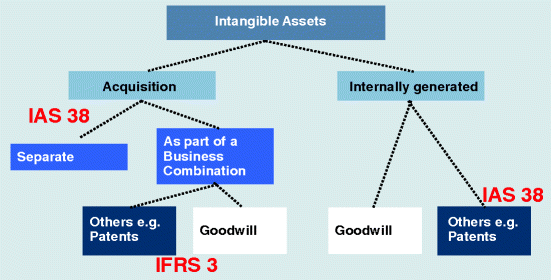
IAS 38 stipulates the recognition criteria in the financial statements for intangible assets which is;
It must be identifiable and to be identifiable it must pass 2 tests;
- It must be separable and
- Must arise from contractual or other legal rights.
Research costs should be expensed off to profit and Loss a/c if it meets the above criteria.
However; most intangible assets are not identifiable and the costs cannot be separated except for Development Expenditure.
Internally generated intangibles such as development expenditure to be capitalized in the Statement of financial position MUST meet certain conditions.
The below acronym will help you classify it correctly;

PIRATE-Internally generated intangibles-Development Expenditure IAS 38
P – Probable that future economic benefits will flow to the entity
I –Intention to complete & use/sell the asset
R –Resources are adequate and available to complete and use/sell the asset
A –Ability to complete or use the asset
T –Technical Feasibility studies have started
E –Expenditure to be incurred can be measured reliably.

When an asset meets the above criteria, it is capitalized as an intangible asset in the statement of financial position at cost and amortized over its useful life.
Also read:https://www.campustimesug.com/?s=ifrs+5
